
 探索發現 · 交大智慧
探索發現 · 交大智慧
上海交大蔡永立教授團隊使用大型語言模型挖掘文化生態系統服務感知:一種小樣本和提示方法

近日,金沙js1005線路設計學院風景園林系蔡永立教授團隊在區域與城市規劃國際頂級期刊《Landscape and Urban Planning》(影響因子7.9,JCR/Q1,中科院SCI一區,Top期刊)發表學術論文“Using large language models to investigate cultural ecosystem services perceptions: A few-shot and method”(使用大型語言模型挖掘文化生態系統服務感知:一種小樣本和提示方法)。本研究提出了一個創新框架,將大語言模型與社交媒體文本相結合,以調查文化生態系統服務的感知。研究結果為廬山景區的景觀管理提供了有價值的見解,展示了大語言模型的優勢、局限性以及在推進景觀感知研究方面的巨大潛力。

圖片摘要
亮點
1. 在沒有大規模訓練數據的情況下自動處理社交媒體文本。
2. 使用大型語言模型識別文化生態系統服務和對應的情感。
3. 通過設計提示提高模型性能。
4. 繪制文化生態系統服務地圖為景觀管理提供見解。
5. 強調了大型語言模型在景觀感知研究中的潛力。
背景
生成式人工智能的進步對社會的各個方面產生了深遠的影響,包括科學研究,但其在景觀研究中的應用仍未得到充分探索。本研究使用大型語言模型來分析文化生態系統服務,這是人類與自然之間的關鍵聯系,反映了生態系統提供的無形利益。
方法
廬山風景區以豐富的文化生態系統服務而聞名,本研究選擇發布在該區域內的社交媒體文本進行分析。該方法涉及小樣本學習,用于調整模型從而對文化生態系統服務及其對應的情感進行分類,同時,設計提示以優化模型性能。本研究比較了三個基本模型和五個提示的性能。最后,根據模型輸出分析了研究區域內的文化生態系統服務感知。
結果
Moonshot-v1-8k模型性能出色,實現了82.2%的micro-F1和80.3%的macro-F1。思維鏈提示和文化生態系統服務定義提示分別增強了6.3%的micro-F1和3.3%的macro-F1。廬山風景區的美學服務是最常見的感知類別,而游憩服務的負面感知最強。新冠疫情后,公眾對身體健康相關服務的興趣增加。
貢獻
本研究考察了大型語言模型在分析文化生態系統服務感知中的應用和可靠性。通過提供一種新的文本分析方法,研究為景觀管理提供了有價值的見解,并強調了人工智能技術在景觀研究中的適用性和潛力
關鍵詞
文化生態系統服務;社交媒體文本;情感分析;語義分析;小樣本學習
Abstract
The advancement of generative AI has profoundly impacted various aspects of society, including scientific research, but its application in landscape research remains underexplored. In this study, large language models are applied to analyze cultural ecosystem services, which are a key connection between humans and nature, reflecting the intangible benefits that ecosystems provide. Social media texts from the Lushan Scenic Area, known for its rich cultural ecosystem services, were analyzed. The methodology involved adapting the model using few-shot learning to classify cultural ecosystem services and associated sentiments. Prompts were specifically designed to optimize model performance. The validation process compared the performance of three base models (GLM-4-0520, ERNIE-4.0—8K, and Moonshot-v1-8k) alongside five prompts. The cultural ecosystem services within the study area were subsequently analyzed based on model outputs. The findings indicated superior performance by the Moonshot-v1-8k model, achieving 82.2 % micro-F1 and 80.3 % macro-F1. The implementation of chain-of-thought prompts and cultural ecosystem services definition prompts enhanced micro-F1 and macro-F1 by up to 6.3 % and 3.3 %, respectively. Within the Lushan Scenic Area, aesthetic services were identified as the most frequently perceived, while recreational services received the most negative sentiments. A marked increase in public interest in physical health was observed following the COVID-19 pandemic. This study highlights the potential of large language models to advance the analysis of cultural ecosystem services and landscape perceptions. By offering a novel approach to text analysis, the findings contribute valuable insights for landscape management and underscore the utility of AI technologies.
Keywords: Cultural ecosystem services; Social media text; Sentiment analysis; Semantic analysis; Few-shot learning
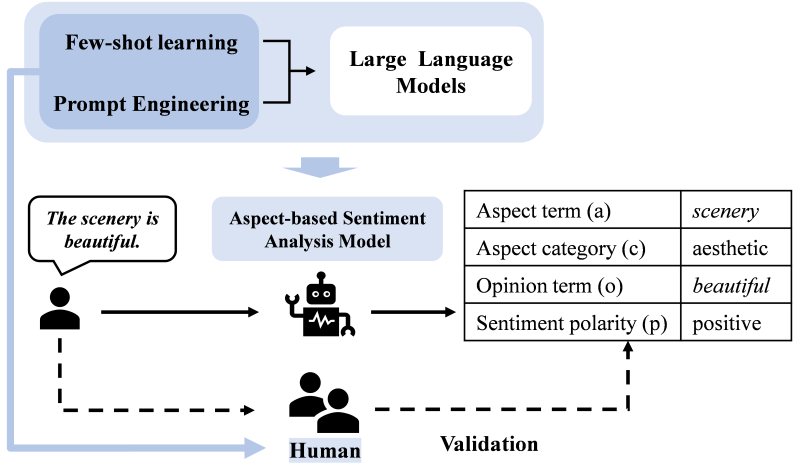
圖1. 概念圖
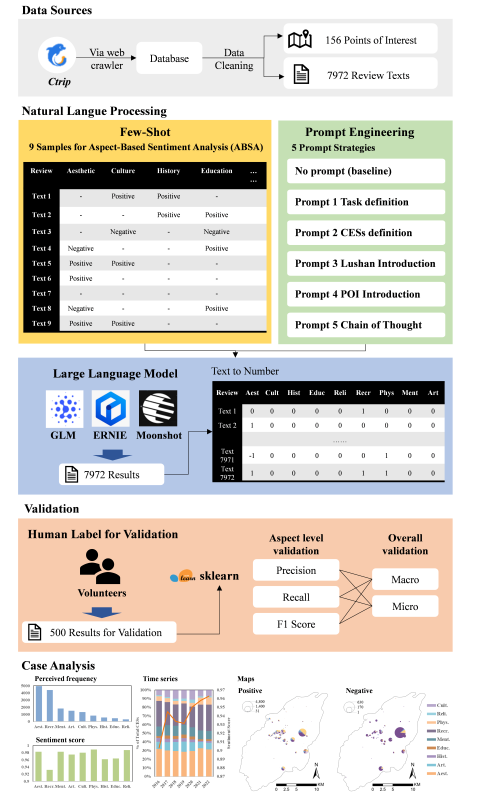
圖2. 研究框架

圖3. 研究區,圖片來源:www.ctrip.com

圖4. 網站界面和評論統計
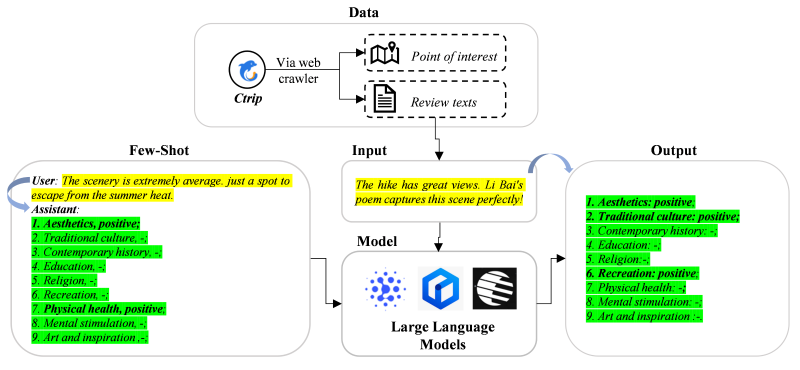
圖5. 小樣本學習示意圖(注:黃色高亮部分表示“模型輸入”(參數:input)對應“小樣本”(參數:user),而綠色高亮表示“模型輸出”(參數:output)對應“小樣本”(參數:assistant))

圖6. 提示示意圖(注:綠色高亮表示“少樣本”(參數:user和assistant)以及相應的模型輸入和輸出(參數:input和outpu);黃色高亮表示“提示”(參數:system);藍色高亮表示“PI 提示”中的“動態提示”,它介紹了每個興趣點,并根據不同的興趣點而變化(參數:system);灰色高亮部分表示“COT 提示”中新增的“關鍵詞”“模型輸出”(參數:Output)對應“小樣本”(參數:assistant))
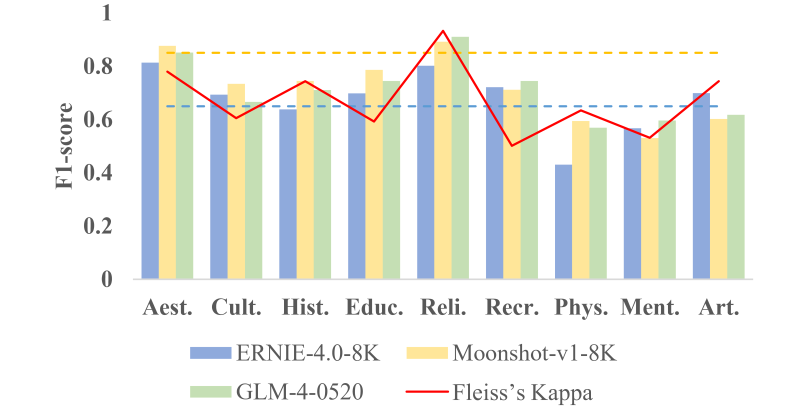
圖7. 不同文化生態系統服務類別的F1-score和Fleiss Kappa

圖8. 廬山景區的文化生態系統服務感知
金沙js1005線路設計學院風景園林專業碩士生羅涵月為論文第一作者,通訊作者為金沙js1005線路設計學院教授蔡永立,論文合作者為金沙js1005線路碩士畢業生張智舵,金沙js1005線路設計學院博士朱青和國際留學生博士Nour El Houda Ben Ameur,以及上海同濟城市規劃設計研究院高級工程師劉曉、中級工程師丁凡。本研究獲得國家自然科學基金青年科學基金項目(72104232)、教育部哲學社科重大項目(19JZD023)以及上海市科學技術委員會軟科學研究項目(23692117800)共同支持。
論文鏈接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2025.105323